Bidyanus bidyanus
 | |
| Estat de conservació | |
|---|---|
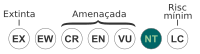 | |
| Gairebé amenaçada | |
| UICN | 2804 |
| Taxonomia | |
| Super-regne | Eukaryota |
| Regne | Animalia |
| Fílum | Chordata |
| Classe | Actinopteri |
| Ordre | Perciformes |
| Família | Terapontidae |
| Gènere | Bidyanus |
| Espècie | Bidyanus bidyanus T.Mitch., 1838 |
| Nomenclatura | |
| Sinònims | |
| Distribució | |
| Endèmic de | |
Bidyanus bidyanus és una espècie de peix pertanyent a la família dels terapòntids.[2]
Descripció[modifica]
Reproducció[modifica]
Té lloc a l'estiu (entre el novembre i el gener, quan la temperatura de l'aigua és al voltant dels 23-30 °C) i després d'una migració aigües amunt. Els ous són pelàgics, fan 2,7-2,8 mm de diàmetre i les larves es desclouen al cap de 30 hores amb una mida de 3,6 mm de longitud.[3][7]
Alimentació[modifica]
Menja insectes aquàtics, mol·luscs, cucs i plantes.[3]
Hàbitat[modifica]
És un peix d'aigua dolça, bentopelàgic, potamòdrom[8] i de clima subtropical (10 °C-30 °C; 29°S-35°S).[3]
Distribució geogràfica[modifica]
Es troba a Austràlia: la conca del Murray-Darling (sud de Queensland, Nova Gal·les del Sud i el sud de Victòria).[3][9][10][11][12]
Observacions[modifica]
És inofensiu per als humans, molt apreciat pels afeccionats a la pesca esportiva i una espècie cada cop més utilitzada en aqüicultura a Austràlia, ja que és bona per al consum humà.[13][14][15][16][17][18][3]
Referències[modifica]
- ↑ Catalogue of Life (anglès)
- ↑ The Taxonomicon (anglès)
- ↑ 3,0 3,1 3,2 3,3 3,4 3,5 FishBase (anglès)
- ↑ Allen, G.R., S.H. Midgley i M. Allen, 2002. Field guide to the freshwater fishes of Australia. Western Australian Museum, Perth, Austràlia Occidental. 394 p.
- ↑ Merrick, J.R. i G.E. Schmida, 1984. Australian freshwater fishes: biology and management. Griffin Press Ltd., Austràlia Meridional. 409 p.
- ↑ Allen, G.R., 1989. Freshwater fishes of Australia. T.F.H. Publications, Inc., Neptune City, Nova Jersey.
- ↑ Breder, C. M.; Rosen, D. E. Modes of Reproduction in Fishes (en anglès). Museu Americà d'Història Natural, 1966.
- ↑ Riede, K., 2004. Global register of migratory species - from global to regional scales. Final Report of the R&D-Projekt 808 05 081. Federal Agency for Nature Conservation, Bonn, Alemanya. 329 p.
- ↑ Arthington, A.H. i F. McKenzie, 1997. Review of impacts of displaced/introduced fauna associated with inland waters. Australia: State of the Environment Technical Paper Series (Inland waters), Department of the Environment, Canberra (Austràlia). 69 p.
- ↑ Eldredge, L.G., 1994. Freshwater fishes. P. 73-84. A: L.G. Eldredge, Perspectives in aquatic exotic species management in the Pacific Islands. Vol. 1. Introductions of commercially significant aquatic organisms to the Pacific Islands. South Pacific Commission, Nova Caledònia.
- ↑ Hoese, D.F., D.J. Bray, J.R. Paxton i G.R. Allen, 2006. Fishes. A Beasley, O.L. i A. Wells (eds.) Zoological Catalogue of Australia. Volum 35. ABRS & CSIRO Publishing: Australia Part 1, pp. xxiv 1-670; Part 2, pp. xxi 671-1472; Part 3, pp. xxi 1473-2178.
- ↑ Paxton, J.R., D.F. Hoese, G.R. Allen i J.E. Hanley, 1989. Pisces. Petromyzontidae to Carangidae. Zoological Catalogue of Australia, Vol. 7. Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, 665 p.
- ↑ Rowland, S.J., 1995. High density pond culture of silver perch, Bidyanus bidyanus. Asian Fish. Sci. 8:73-79.
- ↑ Allen, G.R., S.H. Midgley i M. Allen, 2002.
- ↑ Garibaldi, L., 1996. List of animal species used in aquaculture. FAO Fish. Circ. 914. 38 p.
- ↑ FAO, 1996. Aquaculture production statistics 1985-1994. FAO Fish. Circ. 815. 189 p.
- ↑ FAO Fishery Information, Data and Statistics Service 1993 Aquaculture production (1985-1991). FAO Fish. Circ. 815, Rev. 5. 213 p.
- ↑ Liao, C.-I., H.-M. Su i E.Y. Chang, 2001. Techniques in finfish larviculture in Taiwan. Aquaculture 200(2001):1-31.
Bibliografia[modifica]
- Divisió de Peixos de la Smithsonian Institution. Base de dades de la col·lecció de peixos del Museu Nacional d'Història Natural (en anglès). Smithsonian Institution, 2001.
- Anònim, 2002. Base de dades de la col·lecció de peixos del American Museum of Natural History. American Museum of Natural History, Central Park West, NY 10024-5192, Estats Units.
- Baensch, H.A. i R. Riehl, 1985. Aquarien atlas. Band 2. Mergus, Verlag für Natur- und Heimtierkunde GmbH, Melle, Alemanya. 1216 p.
- Baillie, J. i B. Groombridge (eds.), 1996. 1996 IUCN red list of threatened animals. UICN, Gland, Suïssa. 378 p.
- Golani, D. i D. Mires, 2000. Introduction of fishes to the freshwater system of Israel. Isr. J. Aquacult. / Bamidgeh 52(2):47-60.
- Ma, X., X. Bangxi, W. Yindong i W. Mingxue, 2003. Intentionally introduced and transferred fishes in China's inland waters. Asian Fish. Sci. 16(3&4):279-290.
- Warburton, K., S. Retif i D. Hume, 1998. Generalists as sequential specialists: diets and prey switching in juvenile silver perch. Environ. Biol. Fish. 51(4):445-454.
- Wheeler, A., 1977. Das grosse Buch der Fische. Eugen Ulmer GmbH & Co. Stuttgart. 356 p.
- Wu, H.L., K.-T. Shao i C.F. Lai (eds.), 1999. Latin-Chinese dictionary of fishes names. The Sueichan Press, Taiwan.
Enllaços externs[modifica]
| A Wikimedia Commons hi ha contingut multimèdia relatiu a: Bidyanus bidyanus |
