Epinephelus nigritus
| Hyporthodus nigritus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Estat de conservació | |
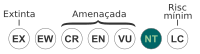 | |
| Gairebé amenaçada | |
| UICN | 7860 |
| Taxonomia | |
| Super-regne | Eukaryota |
| Regne | Animalia |
| Fílum | Chordata |
| Classe | Actinopteri |
| Ordre | Perciformes |
| Família | Serranidae |
| Gènere | Hyporthodus |
| Espècie | Hyporthodus nigritus (Holbrook, 1855) |
| Nomenclatura | |
| Protònim | Serranus nigritus |
Epinephelus nigritus és una espècie de peix de la família dels serrànids i de l'ordre dels perciformes.
Morfologia[modifica]
Els mascles poden assolir els 230 cm de longitud total.[1]
Distribució geogràfica[modifica]
Es troba a l'Atlàntic occidental.[1]
Referències[modifica]
Bibliografia[modifica]
- Baillie, J. i Groombridge, B., 1996. Llista Vermella d'Espècies Amenaçades de la UICN 1996. UICN, Gland, Suïssa.
- Bullock, L.H. i Smith, G.B., 1991. Seabasses (Pisces: Serranidae). Memoirs of the Hourglass Cruises. Volum VIII, Part II. Florida Marine Research Institute, Department of Natural Resources, St. Petersburg, Florida. 243 pp.
- Claro, R., Lindeman, K.C. i Parenti, L.R., 2001. Ecology of the marine fishes of Cuba. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington DC.
- Coleman, F.C. i Williams, S.L., 2002. Overexploiting marine ecosystem engineers: potential consequences for biodiversity. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 17: 40-44.
- Coleman, F.C., Baker, P. i Koenig, C.C., 2004. A review of Gulf of Mexico marine protected areas: successes, failures, and lessons learned. Fisheries 29: 10-21.
- FAO, 1977. FAO species identification sheets, fishing area 31 (W. Cent. Atlantic), núm. Serran Epin 20. FAO, Roma.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2002. FAO yearbook. Fishery statistics: catches and landings. FAO, Roma.
- García-Cagide, A., Claro, R. i Koshelev, B.V., 1994. Reproducción. A: R. Claro (ed.) Ecología de los peces marinos de Cuba, pp. 187-262. Inst. Oceanol. Acad. Cienc. Cuba. and Cen. Invest. Quintana Roo (CIQRO), Mèxic.
- GMFMC, 2003. Commercial Fishing Regulations for Gulf of Mexico Federal Waters. Gulf of Mexico Fishery Management Council, Tampa, Florida: 4.
- Gutherz, E.J., 1982. Reef fish assessment, snapper/grouper stocks in the western north Atlantic south of Cape Hatteras, NC. NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFC-80, pp. 124-141.
- Hardy, J.D., 1978. Development of Fishes of the Mid-Atlantic Bight. Three Volumes. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Office of Biological Services.
- Heemstra, P.C. i Randall, J.E., 1993, Groupers of the World (Family Serranidae, Subfamily Epinephelinae). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of the grouper, rockcod, hind, coral grouper and lyretail species known to date. FAO Species Catalogue Vol. 16., FAO Fish. Synop. Núm. 125, 125:I-viii, 1-382.
- Helfman, G. S.; Collette, B. B.; Facey, D. E. The Diversity of Fishes (en anglès). Blackwell Science, 1997. ISBN 9780865422568.
- Lavett Smith, C., 1971. Revision of the American groupers: Epinephelus and allied genera. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 146(2).
- Manooch III, C.S. i Mason, D.L., 1987. Age and Growth of the Warsaw Grouper and Black Grouper from the southeast region of the United States. Northeast Gulf Science 9(2): 65-75.
- Mazurek, R., 2004. Seafood Watch, Seafood Report, Commercially Important Groupers of the Gulf of Mexico & South Atlantic Regions. Monterey Bay Aquarium.
- Moyle, P.; Cech, J. Fishes: An Introduction to Ichthyology (en anglès). 4a edició. Prentice Hall, 2000. ISBN 9780130112828.
- Musick, J.A., Harbin, M.M., Berkeley, S.A., Burgess, G.H., Eklund, A.M., Findley, L., Gilmore, R.G., Golden, J.T., Ha, D.S., Huntsman, G.R., McGovern, J.C., Parker, S.J., Poss, S.G., Sala, E., Schmidt T.W., Sedberry, G.R., Weeks, H. i Wright, S.G., 2000. Marine, estuarine, and diadromous fish stocks at risk of extinction in North America (Exclusive of Pacific Salmonids). Fisheries 25(11): 6-30.
- National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), 2003. Final Amendment 13A to the Fishery Management Plan for the Snapper Grouper Fishery of the South Atlantic Region. Includes an Environmental Assessment, Initial Regulatory Flexibility Analysis, Regulatory Impact Review and Social Impact Assessment/Fishery Impact Statement. National Marine Fisheries Service, Charleston, Carolina del Sud.
- Nelson, J. S. Fishes of the World (en anglès). 3a edició. Wiley, 1994. ISBN 978-0-471-54713-6.
- Parker, R.O. i Mays, R.W., 1998. Southeastern U.S. deepwater reef fish assemblages, habitat characteristics, catches, and life history summaries. NOAA Technical Report NMFS 138, pp. 1-41.
- Richards, W.J., 1999. Preliminary guide to the identification of the early life history stages of serranid fishes of the western central Atlantic. NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-419.
- Robins, C.R. i Ray, G.C., 1986. A field guide to Atlantic coast fishes of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston.
- SAFMC, 2003. Commercial Fishing Regulations for South Atlantic Federal Waters. South Atlantic Fishery Management Council, Miami, Florida: 4.
- Wheeler, A. The World Encyclopedia of Fishes (en anglès). 2a edició. Macdonald, 1985. ISBN 978-0356107158.
Enllaços externs[modifica]
| A Wikimedia Commons hi ha contingut multimèdia relatiu a: Epinephelus nigritus |
- ITIS (anglès)
