Fitxer:Fasciola LifeCycle.gif
Fasciola_LifeCycle.gif (568 × 435 píxels, mida del fitxer: 58 Ko, tipus MIME: image/gif)
Historial del fitxer
Cliqueu una data/hora per veure el fitxer tal com era aleshores.
| Data/hora | Miniatura | Dimensions | Usuari/a | Comentari | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| actual | 21:05, 9 jul 2015 |  | 568 × 435 (58 Ko) | CFCF | updated |
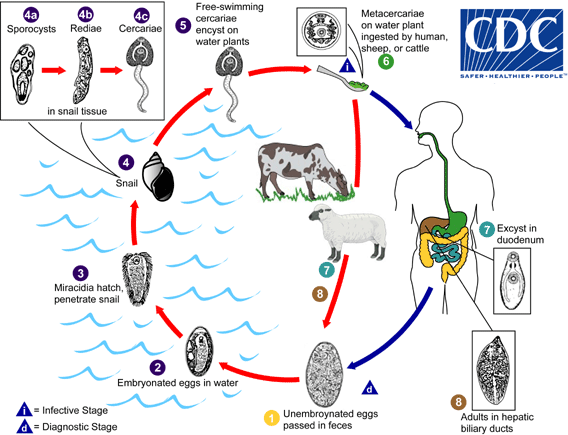
| 18:59, 10 maig 2006 |  | 568 × 435 (45 Ko) | Patho | {{Information| |Description=Causal Agents: The trematodes Fasciola hepatica (the sheep liver fluke) and Fasciola gigantica, parasites of herbivores that can infect humans accidentally. Life Cycle: Life cycle of Fasciola hepatica Immature eggs are disch |
Ús del fitxer
Les 2 pàgines següents utilitzen aquest fitxer:
Ús global del fitxer
Utilització d'aquest fitxer en altres wikis:
- Utilització a ceb.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a cs.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a de.wikibooks.org
- Utilització a es.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a fr.wiktionary.org
- Utilització a gl.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a gl.wiktionary.org
- Utilització a hi.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a it.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a kk.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a ru.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a se.wikimedia.org
- Utilització a sv.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a vi.wikipedia.org
- Utilització a vi.wiktionary.org