Alfa-sinucleïna
L'alfa-sinucleïna (α-sinucleïna) és una proteïna petita de 140 aminoàcids amb un pes molecular de 14.460 Da. Representa més de l'1% de la proteïna total en el cervell. També es troba en grans quantitats a la medul·la òssia i en menor proporció als ovaris, l'endometri, placenta, pròstata, pell, melsa i tiroide.[6]
Forma part de la família de les nucleïnes,[7] té una estructura terciària dinàmica, comparteix el 61% d'homologia de seqüència[8] amb la beta-sinucleïna i es manté en alt grau entre les espècies de vertebrats.[9] No posseeix una seqüència de senyal, el que suggereix que és una proteïna intracel·lular.[10]
Existeix tota una sèrie de mètodes immunohistoquímics per identificar-la adequadament als teixits.[11][12]
Localització cromosòmica
[modifica]Està codificada pel gen SNCA[13] localitzat en el braç llarg del cromosoma 4, en humans (4q21.3-q22).[14] El control de la seva expressió ve donat per la beta-sinucleïna,[15] una altra proteïna intrínsecament desestructurada que interactua a diversos nivells amb l'alfa sinucleïna.[16]
Dominis
[modifica]La proteïna es divideix en tres regions o segments amb diferents propietats i funcions:[17]
• Del residu 1 al 70 es troba el segment N-terminal. És una zona amfipàtica, carregada positivament, molt important en l'oligomerització induïda per àcids grassos de les seves molècules.[18]
• Del residu 71 al 82 es troba la regió central hidrofòbica. Es pensa que és la responsable de l'agregació proteica.[19]
• Del residu 83 al 140 es troba la regió C terminal. Té una gran quantitat de grups carboxils i presenta càrrega negativa. A banda d'altres accions, estabilitza determinades estructures no fibril·lars de la proteïna.[20]
Estructura
[modifica]Estructura primària
[modifica]És una seqüència lineal dels aminoàcids següents:
MDVFMKGLSK - AKEGVVAAAE - KTKQGVAEAA - GKTKEGVLYV - GSKTKEGVVH (50)
GVATVAEKTK - EQVTNVGGAV - VTGVTAVAQK - TVEGAGSIAA - ATGFVKKDQL (100)
GKNEEGAPQE - GILEDMPVDP - DNEAYEMPSE - EGYQDYEPEA (140)
Estructura secundària
[modifica]Està conformada per hèlixs alfa i làmines beta.
- L`estructura hèlix alfa es pot trobar entre els aminoàcids: 3-11, 17-19, 21-32, 41-44, 52-55, 66-68.
- Les làmines beta es localitzen entre els aminoàcids: 45-47, 70-78, 80-83, 88-98, 110-113.
També es poden trobar parts amb girs, entre els aminoàcids 120-122, 124-126, i zones sense estructura representada.[21]
Funcions
[modifica]Les funcions d'aquesta proteïna estan relacionades amb la seva conformació i encara que es desconeixen moltes d'elles es creu que l'alfa-sinucleïna està implicada en:[22]
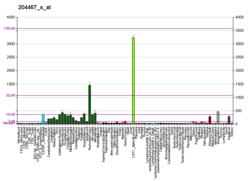
- El reciclatge de vesícules. Això s'infereix perquè s'han trobat grans concentracions d'aquesta proteïna en aquestes àrees.[24]
- La regulació de transmissió de senyals en zones presinàptiques. La hipòtesi generalment acceptada és que compleix aquesta funció perquè té un paper essencial en l'ordenació de les vesícules durant la neurotransmissió.[25] Es creu que hi ha dues regions d'aquesta proteïna capaços d'adherir-se a vesícules, regulant d'aquesta manera el nombre de vesícules emprades en cada transmissió.[26]
- També s'ha comprovat que l'alfa-sinucleïna intervé en l'apoptosi neuronal,[27] la plasticitat neuronal,[28] l'activació de cèl·lules de la micròglia[29] i participa en la biosíntesis, metabolisme i secreció de la dopamina.[30]
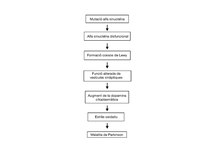
- En el cas de que aquesta proteïna pateixi mutació o disfunció pot provocar la formació dels cossos de Lewy (agregats intraneuronals proteínics anormals, identificables microscòpicament com a masses esfèriques eosinòfiles que desplacen a la resta de components cel·lulars),[31] els quals originen la malaltia de Parkinson.[32][33]
Importància biomèdica
[modifica]Les mutacions més comunes del gen SNCA[34] són A53T,[35] A30P,[36] E46K,[37] H50Q,[38] G51D,[39] A53E[40] i A53V,[41] que són autosòmiques dominants.[42] Aquestes mutacions donen lloc a una forma aberrant de la proteïna. A més de les mutacions, els duplicats[43] o triplicats[44] del gen condueixen a un excés de alfa-sinucleïna que poden generar agregats que provoquen seriosos danys neuronals.[45]
Quan es formen agregats de alfa-sinucleïna, la proteïna nativa perd la seva funció i guanya toxicitat al convertir-se en oligòmer donant lloc a l'espècie tòxica[46][47] que forma fibres de alfa-sinucleïna i és la causant de la destrucció de les neurones dopaminèrgiques de la substància negra cerebral.[48]
A banda del cervell, en la malaltia de Parkinson es troben agregats en els ganglis simpàtics, el nervi vague, el tracte gastrointestinal, les glàndules suprarenals, el greix i al cor. L'alfa-sinucleïna es considera tant un biomarcador diagnòstic com un potencial objectiu terapèutic en aquesta patologia, ja que és la principal responsable de la degradació selectiva de les neurones característica del procés parkinsonià[49] i d'altres sinucleïnopaties relacionades.[50] En aquest sentit, una de les principals línies de recerca biomèdica emergents en el camp de les malalties neurodegeneratives és el disseny de nous compostos capaços de modular eficaçment l'agregació de l'alfa-sinucleïna.[51][52]
Ara per ara, la influència que pot tenir aquesta proteïna -tant de forma activa com passiva- en la patofisiologia de la malaltia d'Alzheimer no es coneix clarament.[53] S'investiguen les seves possibles interaccions a nivell cel·lular amb la proteïna Tau.[54][55] Certes anomalies en l'agregació de l'alfa-sinucleïna també semblen estar associades a la gènesi de la síndrome dels moviments oculars ràpids (un tipus de trastorn del son)[56] i de l'Atròfia multisistèmica.[57]
Referències
[modifica]- ↑ «Malalties que s'associen genèticament amb SNCA, vegeu/editeu les referències a wikidata».
- ↑ 2,0 2,1 2,2 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000145335 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ 3,0 3,1 3,2 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025889 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ «Human PubMed Reference:». National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ «Mouse PubMed Reference:». National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Ltic S, Perovic M, Mladenovic A, Raicevic N, et al «Alpha-synuclein is expressed in different tissues during human fetal development» (en anglès). J Mol Neurosci, 2004; 22 (3), pp: 199-204. ISSN 0895-8696. DOI: 10.1385/jmn:22:3:199. PMID: 14997013 [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ Lavedan, C «The Synuclein Family» (en anglès). Genome Res, 1998 Set; 8 (9), pp: 871-880. ISSN 1549-5469. DOI: 10.1101/gr.8.9.871. PMID: 9750188 [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ Pearson, WR «An introduction to sequence similarity ("homology") searching» (en anglès). Curr Protoc Bioinformàtics, 2013 Jun; Chapter 3: Unit 3.1, pàgs: 9. PMID: 23749753. DOI: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0301s42. PMC: 3820096 [Consulta: 5 abril 2020].
- ↑ Pernick, N «Alpha-synuclein» (en anglès). Stains & molecular markers. PathologyOutlines, Inc, 2019; Mar 4 (rev), pàgs: 3 [Consulta: 14 març 2020].
- ↑ Leica Biosystems «Alpha-Synuclein» (en anglès). IHC Primary Antibodies, 2019, pàgs: 2 [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ Beach TG, White CL, Hamilton RL, Duda JE, et al «Evaluation of α-synuclein immunohistochemical methods used by invited experts» (en anglès). Acta Neuropathol, 2008 Set; 116 (3), pp: 277-288. DOI: 10.1007/s00401-008-0409-8. PMC: 2708176. PMID: 18626651 [Consulta: 17 març 2020].
- ↑ Corbillé AG, Letournel F, Kordower JH, Lee J, et al «Evaluation of alpha-synuclein immunohistochemical methods for the detection of Lewy-type synucleinopathy in gastrointestinal biopsies» (en anglès). Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2016 Abr 4; 4, pp: 35. DOI: 10.1186/s40478-016-0305-8. PMC: 4820972. PMID: 27044604 [Consulta: 27 abril 2020].
- ↑ Gene «SNCA synuclein alpha [Homo sapiens (human)]» (en anglès). National Center for Biotechnology Information, US National Library of Medicine, 2019; 31 Des, ID6622 (rev), pàgs: 9 [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ Elcoroaristizabal Martín X, Gómez Busto F, González Fernández MC, de Pancorbo MM «Papel de la genética en la etiología de las sinucleinopatías» (en castellà). Rev Esp Geriatr Gerontol, 2011 Oct; 46 (Supl 1), pp: 3-11. ISSN 1578-1747. DOI: 10.1016/j.regg.2011.10.002. PMID: 22152908 [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ UniProt «Beta-synuclein» (en anglès). Protein knowledgebase. UniProt Consortium, 2019 Des 11; Q16143 -SYUB_HUMAN- (rev), pàgs: 10 [Consulta: 5 gener 2020].
- ↑ Williams JK, Yang X, Baum J «Interactions between the Intrinsically Disordered Proteins β-Synuclein and α-Synuclein» (en anglès). Proteomics, 2018 Nov; 18 (21-22), pp: e1800109. DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201800109. PMC: 6447293. PMID: 30142698 [Consulta: 5 gener 2020].
- ↑ Villegas Pedraza, NL; Chávez Montes, A; Montiel Condado, D; González Hernández, B; González-Horta, A «Análisis funcional de oligómeros de alfa-sinucleína en la permeabilidad de membranas» (en castellà). Acta Bioquím Clín Latinoam, 2014 Des; 48 (4), pp: 437-445. ISSN 1851-6114 [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ Karube H, Sakamoto M, Arawaka S, Hara S, et al «N-terminal region of alpha-synuclein is essential for the fatty acid-induced oligomerization of the molecules» (en anglès). FEBS Lett, 2008 Oct 29; 582 (25-26), pp: 3693-700. ISSN 1873-3468. DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.10.001. PMID: 18848547 [Consulta: 21 abril 2020].
- ↑ Waxman EA, Mazzulli JR, Giasson BI «Characterization of Hydrophobic Residue Requirements for α-Synuclein Fibrillization» (en anglès). Biochemistry, 2009 Oct 13; 48 (40), pp: 9427-9436. DOI: 10.1021/bi900539p. PMC: 2758333. PMID: 19722699 [Consulta: 9 abril 2020].
- ↑ Hong DP, Xiong W, Chang JY, Jiang C, et al «The role of the C-terminus of human α-synuclein: intra-disulfide bonds between the C-terminus and other regions stabilize non-fibrillar monomeric isòmers» (en anglès). FEBS Lett, 2011 Feb 4; 585 (3), pp: 561-566. ISSN 1873-3468. DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.01.009. PMID: 21237164 [Consulta: 24 abril 2020].[Enllaç no actiu]
- ↑ UniProt «Alpha-synuclein» (en anglès). Protein knowledgebase. UniProt Consortium, 2019 Des 11; P37840 -SYUA_HUMAN- (rev), pàgs: 23 [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ Bendor JT, Logan TP, Edwards RH «The function of α-synuclein» (en anglès). Neuron, 2013 Set 18; 79 (6), pp: 1044-1066. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.09.004. PMC: 3866954. PMID: 24050397 [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ Halfon, MJ. «Patogénesis de la enfermedad de Parkinson» (en castellà). Sociedad Neurológica Argentina. Arxivat de l'original el 10 de gener 2020. [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ Patel D, Bordoni B «Physiology, Synuclein» (en anglès). StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing LLC, 2020 Gen 10; NBK553158 (rev), pàgs: 6. PMID: 31985951 [Consulta: 13 març 2020].
- ↑ Perez, RG «The Protein Alpha-Synuclein: Its Normal Role (in Neurons) and Its Role in Disease» (en anglès). Front Neurosci, 2020 Feb 20; 14, pp: 116. DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00116. PMC: 7044239. PMID: 32153354 [Consulta: 13 març 2020].
- ↑ Fusco G, De Simone A, Arosio P, Vendruscolo M, et al «Structural Ensembles of Membrane-bound α-Synuclein Reveal the Molecular Determinants of Synaptic Vesicle Affinity» (en anglès). Sci Rep, 2016 Jun 8; 6, pp: 27125. DOI: 10.1038/srep27125. PMC: 4897633. PMID: 27273030 [Consulta: 13 març 2020].
- ↑ Cookson, MR «α-Synuclein and neuronal cell death» (en anglès). Mol Neurodegener, 2009 Feb 4; 4, pp: 9. DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-4-9. PMC: 2646729. PMID: 19193223 [Consulta: 3 gener 2020].
- ↑ Burré J, Sharma M, Südhof TC «Cell Biology and Pathophysiology of α-Synuclein» (en anglès). Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2018 Mar 1; 8 (3), pii: a024091. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a024091. PMC: 5519445. PMID: 28108534 [Consulta: 14 gener 2020].
- ↑ Ferreira SA, Romero-Ramos M «Microglia Response During Parkinson's Disease: Alpha-Synuclein Intervention» (en anglès). Front Cell Neurosci, 2018 Ag 6; 12, pp: 247. DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00247. PMC: 6087878. PMID: 30127724 [Consulta: 3 gener 2020].
- ↑ Venda LL, Cragg SJ, Buchman VL, Wade-Martins R «α-Synuclein and dopamine at the crossroads of Parkinson's disease» (en anglès). Trends Neurosci, 2010 Des; 33 (12), pp: 559-568. DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.09.004. PMC: 3631137. PMID: 20961626 [Consulta: 3 gener 2020].
- ↑ Mahul-Mellier A, Altay F, Burtscher J, Maharjan, N, et al «The making of a Lewy body: the role of alpha-synuclein post-fibrillization modifications in regulating the formation and the maturation of pathological inclusions» (en anglès). bioRxiv, 2018 Des 19; PPR65370, pàgs: 72. DOI: 10.1101/500058 [Consulta: 6 gener 2020].
- ↑ Kim, WS; Kågedal, K; Halliday, GM «Alpha-synuclein biology in Lewy body diseases» (en anglès). Alzheimers Res Ther, 2014 Oct 27; 6 (5), pp: 73. DOI: 10.1186/s13195-014-0073-2. PMC: 4288216. PMID: 25580161 [Consulta: 23 maig 2020].
- ↑ Engelhardt E, Gomes MDM «Lewy and his inclusion bodies: Discovery and rejection» (en anglès). Dement Neuropsychol, 2017 Abr-Jun; 11 (2), pp: 198-201. DOI: 10.1590/1980-57642016dn11-020012. PMC: 5710688. PMID: 29213511 [Consulta: 2 gener 2020].
- ↑ Genetics Home Reference «SNCA gene» (en anglès). NIH/US National Library of Medicine, 2020; Abr 15 (rev), pàgs: 7 [Consulta: 17 abril 2020].
- ↑ Kang L, Wu KP, Vendruscolo M, Baum J «The A53T mutation is key in defining the differences in the aggregation kinetics of human and mouse α-synuclein» (en anglès). J Am Chem Soc, 2011 Ag 31; 133 (34), pp: 13465-13470. DOI: 10.1021/ja203979j. PMC: 3205953. PMID: 21721555 [Consulta: 16 gener 2020].
- ↑ Lemkau LR, Comellas G, Kloepper KD, Woods WS, et al «Mutant protein A30P α-synuclein adopts wild-type fibril structure, despite slower fibrillation kinetics» (en anglès). J Biol Chem, 2012 Mar 30; 287 (14), pp: 11526-11532. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.306902. PMC: 3322835. PMID: 22334684 [Consulta: 16 gener 2020].
- ↑ Greenbaum EA, Graves CL, Mishizen-Eberz AJ, Lupoli MA, et al «The E46K mutation in alpha-synuclein increases amyloid fibril formation» (en anglès). J Biol Chem, 2005 Mar 4; 280 (9), pp: 7800-7807. ISSN 1083-351X. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M411638200. PMID: 15632170 [Consulta: 16 gener 2020].
- ↑ Khalaf O, Fauvet B, Oueslati A, Dikiy I, et al «The H50Q mutation enhances α-synuclein aggregation, secretion, and toxicity» (en anglès). J Biol Chem, 2014 Ag 8; 289 (32), pp: 21856-21876. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553297. PMC: 4139205. PMID: 24936070 [Consulta: 16 gener 2020].
- ↑ Fares MB, Ait-Bouziad N, Dikiy I, Mbefo MK, et al «The novel Parkinson's disease linked mutation G51D attenuates in vitro aggregation and membrane binding of α-synuclein, and enhances its secretion and nuclear localization in cells» (en anglès). Hum Mol Genet, 2014 Set 1; 23 (17), pp: 4491-4509. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddu165. PMC: 4119404. PMID: 24728187 [Consulta: 16 gener 2020].
- ↑ Lázaro DF, Dias MC, Carija A, Navarro S, et al «The effects of the novel A53E alpha-synuclein mutation on its oligomerization and aggregation» (en anglès). Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2016 Des 9; 4 (1), pp: 128. DOI: 10.1186/s40478-016-0402-8. PMC: 5148884. PMID: 27938414 [Consulta: 17 gener 2020].
- ↑ Mohite GM, Kumar R, Panigrahi R, Navalkar A, et al «Comparison of Kinetics, Toxicity, Oligomer Formation, and Membrane Binding Capacity of α-Synuclein Familial Mutations at the A53 Site, Including the Newly Discovered A53V Mutation» (en anglès). Biochemistry, 2018 Set 4; 57 (35), pp: 5183-5187. ISSN 0006-2960. DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00314. PMID: 29771508 [Consulta: 17 gener 2020].
- ↑ Spillantini MG, Goedert M «Neurodegeneration and the ordered assembly of α-synuclein» (en anglès). Cell Tissue Res, 2018 Jul; 373 (1), pp: 137-148. DOI: 10.1007/s00441-017-2706-9. PMC: 6015613. PMID: 29119326 [Consulta: 15 gener 2020].
- ↑ Kéri S, Moustafa AA, Myers CE, Benedek G, Gluck MA «{alpha}-Synuclein gene duplication impairs reward learning» (en anglès). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010 Set 7; 107 (36), pp: 15992-15994. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1006068107. PMC: 2936644. PMID: 20733075 [Consulta: 19 març 2020].
- ↑ Flierl A, Oliveira LM, Falomir-Lockhart LJ, Mak SK, et al «Higher vulnerability and stress sensitivity of neuronal precursor cells carrying an alpha-synuclein gene triplication» (en anglès). PLoS One, 2014 Nov 12; 9 (11), pp: e112413. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112413. PMC: 4229205. PMID: 25390032 [Consulta: 19 març 2020].
- ↑ Villar-Piqué A, Lopes da Fonseca T, Outeiro TF «Structure, function and toxicity of alpha-synuclein: the Bermuda triangle in synucleinopathies» (en anglès). J Neurochem, 2016 Oct; 139 (Supl 1), pp: 240-255. ISSN 1471-4159. DOI: 10.1111/jnc.13249. PMID: 26190401 [Consulta: 11 maig 2020].
- ↑ Winner B, Jappelli R, Maji SK, Desplats PA, et al «In vivo demonstration that α-synuclein oligomers are toxic» (en anglès). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011 Mar 8; 108 (10), pp: 4194-4199. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1100976108. PMC: 3053976. PMID: 21325059 [Consulta: 7 gener 2020].
- ↑ Rodriguez JA, Ivanova MI, Sawaya MR, Cascio D, et al «Structure of the toxic core of α-synuclein from invisible crystals» (en anglès). Nature, 2015 Set 24; 525 (7570), pp: 486-490. DOI: 10.1038/nature15368. PMC: 4791177. PMID: 26352473 [Consulta: 8 gener 2020].
- ↑ Huenchuguala, S «Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers and Dopamine» (en anglès). Clin Pharmacol Transl Med, 2018 Abr; 2 (1), pp: 84-86. ISSN 2572-7656 [Consulta: 6 gener 2020].
- ↑ Xu L, Pu J «Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease: From Pathogenetic Dysfunction to Potential Clinical Application» (en anglès). Parkinsons Dis, 2016 Ag; 2016, pp: 1720621. DOI: 10.1155/2016/1720621. PMC: 5005546. PMID: 27610264 [Consulta: 3 gener 2020].
- ↑ Brundin P, Dave KD, Kordower JH «Therapeutic approaches to target alpha-synuclein pathology» (en anglès). Exp Neurol, 2017 Des; 298 (Pt B), pp: 225-235. DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.10.003. PMC: 6541231. PMID: 28987463 [Consulta: 5 gener 2020].
- ↑ Paleologou KE, Irvine GB, El-Agnaf OM «Alpha-synuclein aggregation in neurodegenerative diseases and its inhibition as a potential therapeutic strategy» (en anglès). Biochem Soc Trans, 2005 Nov; 33 (Pt 5), pp: 1106-1110. ISSN 0300-5127. DOI: 10.1042/BST20051106. PMID: 16246056 [Consulta: 17 gener 2020].
- ↑ «α-Synuclein aggregation modulation: an emerging approach for the treatment of Parkinson's disease» (en anglès). Future Med Chem, 2017 Jun; 9 (10), pp: 1039-1053. DOI: 10.4155/fmc-2017-0016. PMC: 5941702. PMID: 28632413 [Consulta: 17 gener 2020].
- ↑ Twohig D, Nielsen HM «α-synuclein in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease» (en anglès). Mol Neurodegener, 2019 Jun 11; 14 (1), pp: 23. DOI: 10.1186/s13024-019-0320-x. PMC: 6558879. PMID: 31186026 [Consulta: 14 gener 2020].
- ↑ Yan X, Uronen RL, Huttunen HJ «The interaction of α-synuclein and Tau: A molecular conspiracy in neurodegeneration?» (en anglès). Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2018; Maig 9, pii: S1084-9521(17)30389-0. ISSN 1084-9521. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.05.005. PMID: 29738880 [Consulta: 15 gener 2020].
- ↑ Yeboah F, Kim TE, Bill A, Dettmer U «Dynamic behaviors of α-synuclein and tau in the cellular context: New mechanistic insights and therapeutic opportunities in neurodegeneration» (en anglès). Neurobiol Dis, 2019 Des; 132, pp: 104543. DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104543. PMC: 6834908. PMID: 31351173 [Consulta: 15 gener 2020].
- ↑ Barone DA, Henchcliffe C «Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder and the link to alpha-synucleinopathies» (en anglès). Clin Neurophysiol, 2018 Ag; 129 (8), pp: 1551-1564. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.05.003. PMC: 6495539. PMID: 29883833 [Consulta: 13 març 2020].
- ↑ Monzio Compagnoni G, Di Fonzo A «Understanding the pathogenesis of multiple system atrophy: state of the art and future perspectives» (en anglès). Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2019 Jul 12; 7 (1), pp: 113. DOI: 10.1186/s40478-019-0730-6. PMC: 6624923. PMID: 31300049 [Consulta: 26 març 2020].
Bibliografia
[modifica]- Maroteaux, Luc; Campanelli, James T.; Scheller, Richard H. Synuclein: a neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal (en anglès). J Neurosci, 1988 Ag 1; 8 (8), pp: 2804–2815. PMID: 3411354. DOI 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-08-02804.1988 [Consulta: 3 gener 2020].
- Martínez Rivera, Marta; Menéndez González, Manuel; López-Muñiz, Alfonso. Alteraciones neuropsicológicas en las α-sinucleinopatías (en castellà). Archivos de Medicina, 2011; 7 (1), pp: 1-9. ISSN 1698-9465. DOI 10:3823/064 [Consulta: 5 gener 2020].
- Peelaerts, Wouter; Baekelandt, Veerle. ɑ-Synuclein strains and the variable pathologies of synucleinopathies (en anglès). J Neurochem, 2016 Oct; 139 (Supl 1), pp: 256-274. PMID: 26924014. DOI 10.1111/jnc.13595 [Consulta: 3 gener 2020].
- Álvarez García, Paloma. Alfa-sinucleína como diana en el diseño de fármacos -Treball de Fi de Grau- (en castellà). Facultad de Farmacia, UCM, 2018; Jun, pàgs: 40. [Consulta: 3 gener 2020].
- Urrea Zazurca, Laura. Funciones de la proteína priónica celular, alfa-sinucleína y reelina en enfermedades neurodegenerativas -Tesi Doctoral- (en castellà). Departament de Biologia Cel·lular, Fisiologia i Immunologia, Universitat de Barcelona, 2018; Mar, pàgs: 203. [Consulta: 3 gener 2020].
- Guerrero-Ferreira, Ricardo; Taylor, Nicholas MI.; Mona, Daniel; Ringler, Philippe; et al. Cryo-EM structure of alpha-synuclein fibrils (en anglès). eLife, 2018 Jul; 7, pp: e36402. PMID: 29969391. DOI 10.7554/eLife.36402 [Consulta: 7 gener 2020].
- Jęśko, Henryk; Lenkiewicz, Anna M.; Wilkaniec, Anna; Adamczyk, Agata. The interplay between parkin and alpha‑synuclein; possible implications for the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (en anglès). Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars), 2019; 79 (3), pp: 276-289. PMID: 31587020 ISSN 0065-1400 [Consulta: 7 maig 2020].
Enllaços externs
[modifica]- Alpha Synuclein Antibody Staining Protocol for Immunohistochemistry Arxivat 2020-01-06 a Wayback Machine. IHCWorld; 2011. (anglès)
- Una proteína de la enfermedad de Parkinson, vital en el cerebro sano Infosalus.com; 2016 Set. (castellà)
- Alpha-Synuclein - What's it all about? Ruffmann, C. Oxford Parkinson's Disease Centre; 2016 Jul. (anglès)
- Parkinson's disease: alpha-synuclein, a major factor? France Parkinson; 2018 Jul. (anglès)